| Harmonic | Harmonic | |
Sympsionics Symbol | ||
Harmony
Harmonics - "The aliquot part of a complex or compound wave form always multiples of the fundamental." ACOUSTICS § 15, 16
| Mode | Subdivision | Particle |
| Dominant | Etheric | Etheron |
| Harmonic | atomic | Atom |
| Enharmonic | Molecular | molecule |
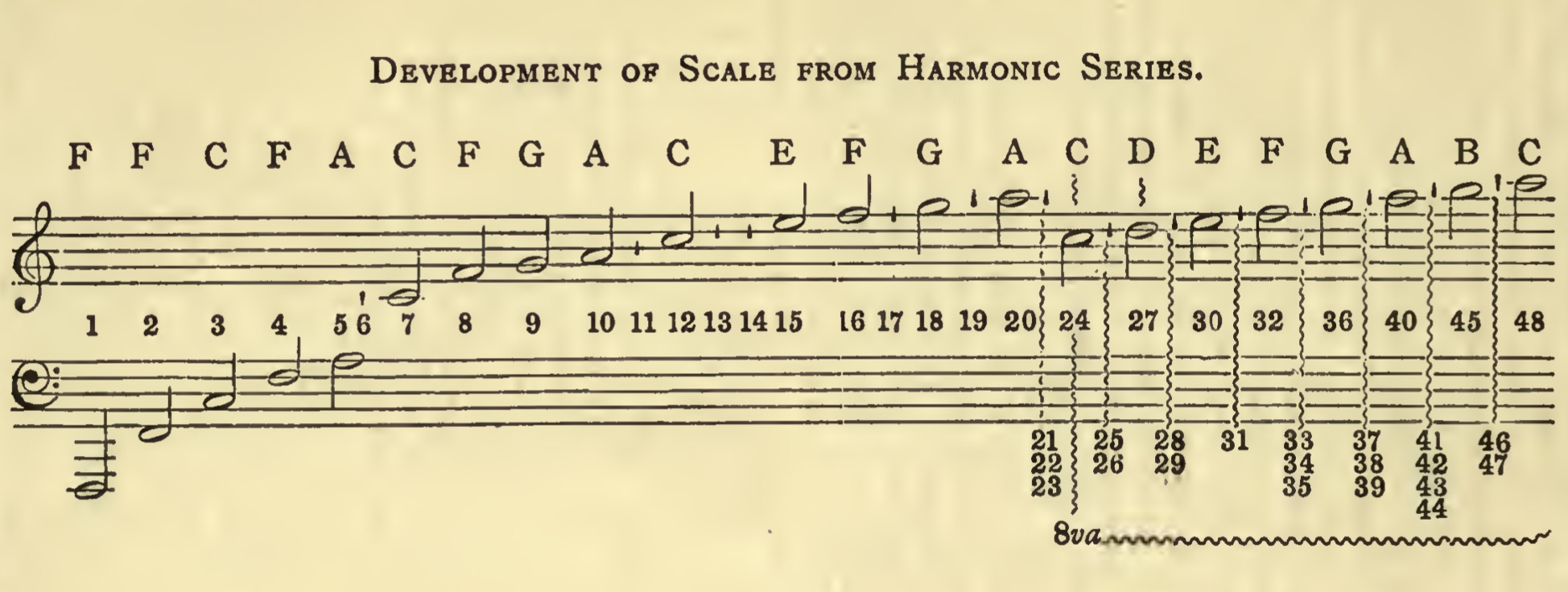
Harmonic Scale
"A harmonic scale is formed by taking a series of notes produced by vibrations whose numbers in a given time are respectively as 1, 2, 3, 4, etc. If we take as fundamental tone the open C string of the violoncello, the series of tones which with it form a harmonic scale will be as pictured.
"The scale formed by a series of natural harmonics. It should be noted that our conventional music scale is a melodic modification of a naturally occurring harmonic scale or series of naturally occurring tones.
"As the character of a sound depends upon that of the vibrations by which it is caused, it is important to know of what kind the latter must be in order that they may give the sensation of a perfectly simple tone, i.e., one which the ear cannot resolve into any others. Such a vibration is perhaps best realised by comparison with that of the pendulum of a clock when it is swinging only a little to and fro. Under these circumstances it is performing what are called harmonic vibrations, and when the air particles in the neighborhood of the ear are caused by any means to vibrate according to the same law as that which the pendulum follows, and also with sufficient rapidity, a perfect simple tone is the result. Such a tone is, however, rarely heard except when produced by means specially contrived for the purpose. If a note on the pianoforte is struck, the impact of the hammer on the string throws it into a state of vibration, which, though periodic, is not really harmonic; consequently we do not hear a perfectly simple tone, but one which is in reality a mixture of several higher simple tones with that one which corresponds to the actual length of the string. The former are, however, generally faint, and become associated by habit with the latter, appearing to form with it a single note of determinate pitch. These higher tones are harmonics of the string, and are produced by vibrations whose numbers per second are respectively twice, three times, four times, etc., as great as those of the fundamental tone of the string." [A Dictionary of Musical Terms; Novello, Ewer and Co., London, pre-1900]
Currents
"The Harmonic chord is the third current of the terrestrial stream." [Keely]
Keely
All the forces of nature, writes Keely, proceed from the one governing force; the source of all life, of all energy. These sympathetic flows, or streams of force, each consists of three currents, harmonic, enharmonic, and dominant; this classification governing all orders of positive and negative radiation. The sympathetic flow called "Animal Magnetism" is the transmissive link of sympathy in the fourth, or interatomic, subdivision of matter. It is the most intricate of problems to treat philosophically; isolated as it is from all approach by any of the prescribed rules in "the orthodox scheme of physics." It turns upon the interchangeable subdivision of interatomic acting agency, or the force of the mind. The action of this etheric flow, in substance of all kinds, is according to the character of the molecular interferences which exist in the volume of their atomic groupings. These interferences proceed from some description of atomic chemical nature, which tend to vary the uniformity of structure in the atomic triplets of each molecule. If these groupings were absolutely uniform there would be but one substance in nature, and all beings inhabiting this globe would be simultaneously impressed with the same feelings and actuated by the same desires; but nature has produced unlimited variety. Since, as yet, has not made so much as an introductory attempt to solve this problem of "the mind flow," but has left it with the hosts of impostors, who always beset any field that trenches on the land of marvel. [Vibratory Physics - The Connecting Link between Mind and Matter]
"Harmonic sympathetic evolution indicates the atom is of wonderfully complex structure. The progressive disintegratory steps in the molecular and intermolecular fields also indicates wonderfully complex structure of those subdivisions." [Keely, Snell Manuscript]
"Reception and dispersion are kept up on the atmospheric envelope of the earth by the atomic and interatomic conflict as "between the dominant and the enharmonic". This is brought about by the reception and dispersion of sympathetic streams, the ruling mode of whose vibration is the dominant, and the density of the coarser grades of matter, whose ruling vibratory mode is the enharmonic.
As every mass consists of vibrations in thirds, balanced in harmonic equilibrium without cancellation or diminution of energy, it stands therefore in harmonic relation to every other mass. All forms of matter and of motion are thus interrelated and interchangeable. Through resonance, increasing this sympathy, we can control the states of matter." [Mass Action, Snell Manuscript - the book]
"All vibrations that are negative in their character as toward destroying the harmonic relations that exist between the magnetic current and its coincident polar, to carry out the simile, close up the aperture whereby illumination (or transfer) is continuously conducted.
The thirds, on the subdivision of the one hundred and twenty-eight thousand four hundred vibrations, represent the negative antagonism, whereby this peculiar condition is brought about, viz., forty-two thousand eight hundred on the positive; the same on the negative and on the neutral, as associated with the sympathetic negative transmitter.
The keeper is first placed on the magnet, which has an attachment whereby a transmitter can be centrally associated with it; the other terminal having three connections that can be attached to this medium. The impulse is given simultaneously to the three leads after setting the instrument to represent forty-two thousand eight hundred vibrations on the harmonic, the same on the enharmonic and on the diatonic.
If this impulse is given properly, the neutralization will take place within fifteen seconds." [The Operation of the Vibratory Circuit]
"The flow of electricity, as set down in Keely's system, is governed by triple conditions: 1st. the dominant or high vibratory; 2nd. the subdominant or low vibratory; 3rd. the harmonic or undulatory; In combination one flow, Keely writes:- "When electrical experts can construct a mechanical device whereby the low vibratory conditions of the subdominant can be assimilated to the harmonic undulatory, by thirds, they will be able to run their dynamos without any extraneous appliances. An introductory impulse, on a certain order of vibration, being all that would be required to give the subdominant a concordant relation to the dominant; which would more effectually operate the dynamo than any number of steam-engines; allowing the harmonic stream to be the governor. This concordance, as towards the dominant, would only excite its sympathetic action in a way that would divert the ruling conditions of the two, without being submitted to the destructive effects of the dominant current. I think many lives will be lost before such a position is attained. Tesla has reached out almost to the crest of the harmonic wave, leaving all electrical explorers far behind him. It is only when such a condition is reached that the true value of electrical lighting will be understood, and extraneous power dispensed with; but, in my opinion, the present conditions for transferring power will remain unaltered, in the use of electricity, for generations." [Appendix II]
"Electricity is the result of three differentiated sympathetic flows, combining the celestial and terrestrial flows by an order of assimilation negatively attractive in its character. It is one of Nature's efforts to restore attractive differentiation. In analyzing this triple union in its vibratory philosophy, I find the highest order of perfection in this assimilative action of Nature. The whole condition is atomic, and is the introductory one which has an affinity for terrestrial centers, uniting magnetically with the Polar stream, in other words, uniting with the Polar stream by neutral affinity. The magnetic or electric forces of the earth are thus kept in stable equilibrium by this triune force, and the chords of this force may be expressed as:
1st.: The Dominant
2nd.: The Harmonic
3rd.: The Enharmonic. [WHAT IS ELECTRICITY]
The value of each is, one to the other, in the rates of figures, true thirds. E flat- transmissive chord or dominant; A flat- harmonic; A double flat- enharmonic. The unition of the two prime thirds is so rapid, when the negative and the positive conditions reach a certain range of vibratory motion, as to be compared to an explosion. During this action the positive electric stream is liberated and immediately seeks its neutral terrestrial center, or center of highest attraction." [Vibratory Physics - The Connecting Link between Mind and Matter]
""Concordance of vibrations on harmonic levels as in the action of gravity." [Keely and His Discoveries, pg 302]
"Keely estimates that, after the introductory impulse is given on the harmonic thirds, molecular vibration is increased from 20,000 per second to 100,000,000." [Snell Manuscript]
"The sympathetic acoustic impulses are:
"the DOMINANT - a diatonic third -
"the HARMONIC - the connective "sixth" - and
"the ENHARMONIC - or diminished seventh - which Keely calls a ninth -
"inducing "infinite trajective velocity" or "neutral radiation" from neutral centers. [Snell Manuscript]
"The fundamental mode of vibration changes in the atomic subdivision to the harmonic, or true fifth of the mass chord.'' [ATOMIC THIRD SUBDIVISION]
"All the forces of nature, writes Keely, proceed from the one governing force; the source of all life, of all energy. These sympathetic flows, or streams of force, each consists of three currents, harmonic, enharmonic, and dominant; this classification governing all orders of positive and negative radiation." [Vibratory Physics - The Connecting Link between Mind and Matter]
"In analyzing this triple union in its vibratory philosophy, I find the highest order of perfection in this assimilative action of Nature. The whole condition is atomic, and is the introductory one which has an affinity for terrestrial centres, uniting magnetically with the Polar stream, in other words, uniting with the Polar stream by neutral affinity. The magnetic or electric forces of the earth are thus kept in stable equilibrium by this triune force, and the chords of this force may be expressed as 1st, the dominant, 2nd, the harmonic, and 3rd, the enharmonic. The value of each is, one to the other, in the rates of figures, true thirds. Eb, - transmissive chord or dominant; Ab - harmonic; Abb - enharmonic. The unition of the two prime thirds is so rapid, when the negative and the positive conditions reach a certain range of vibratory motion, as to be compared to an explosion. During this action the positive electric stream is liberated, and immediately seeks its neutral terrestrial centre, or centre of highest attraction." [True Science]
"Given that force can be exerted by an act of will, do we understand the mechanism by which this is done? And if there is a gap in our knowledge between the conscious idea of a motion and the liberation of muscular energy needed to accomplish it, how do we know that a body may not be moved without ordinary material contact by an act of will? Keely contends that all metallic substances after having been subjected to a certain order of vibration may be so moved. "Scientists are verging rapidly toward the idea that immense volumes of energy exist in all conditions of corpuscular space. I accept Prof. Stoney's idea that an apsidal motion might be caused by an interaction between high and low tenuous matter, but such conditions, even of the highest accelerated motion are too far down below the etheric realm to influence it sympathetically, even in the most remote way. The conception of the molecule disturbing the ether, by electrical discharge from its parts is not correct... the highest conditions associated with electricity come under the fourth descending order of sympathetic conditions. The conjecture as regards the motion being a series of harmonic elliptic ones, accompanied by a slow apsidal one, I believe to be correct... The combination of these motions would necessarily produce two circular motions of different amplitudes whose differing periods might correspond to two lines of the spectrum as conjectured, and lead the experimenter, perhaps, into a position corresponding to an ocular illusion. Every line of the spectrum, I think, consists not of two close lines, but of compound triple lines; though not until an instrument has been constructed, which is as perfect in its parts as is the sympathetic field that environs matter, can any truthful conclusion be arrived at from demonstration." [Keely] [FORCE - Snell]
Partial, Overtone
"If a violin string is bowed steadily, the frequencies of the partials of the resulting complex tone will be integral multiples of the lowest fundamental frequency, and the partials may properly be called harmonics. If, however, the same string is struck or plucked and then allowed to vibrate freely, the frequencies of the partials in the airborne sound and the frequencies of the corresponding modes of vibration are, in general, no longer exactly in the ratios of integers, and the partials and modes of vibration are inharmonic." [A Dictionary of Musical Terms; Novello, Ewer and Co., London, pre-1900]
"Modes of vibration whose frequencies are multiples of the frequency of the fundamental mode." [The Science of Sound; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, 1982.]
"Sinusoidal quantity at a frequency which is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency." [Field of Rotating Machinery Measurement, Monitoring and Analysis; Bentley Nevada Corporation]
Ramsay
HARMONICS ON THE VIOLIN.
At the middle of the string the stopped note and the harmonic notes are the same; but corresponding places above and below the middle give the same harmonic, although these places when stopped give different notes. [Scientific Basis and Build of Music, page 92]
Nine-tenths of a string, if stopped and acted on, gives a tone the ratio of 9:10, but if touched and acted on as a harmonic it gives a note which is three octaves and a major third above the whole string. If the remaining tenth of the string be acted on either as a stopped note or a harmonic it will give the same note which is three octaves and a major third above the whole string the ratio of 1:10, so that the stopped note of one-tenth and the harmonic of nine-tenths are the same. Indeed the bow acting on stopped note of one-tenth, on harmonic of nine-tenths, or on harmonic of one-tenth, produces the same note, as the note is the production of one-tenth in each case; for in the harmonic, whether you bow on the nine-tenths or the one-tenth, while it is true that the whole string is brought into play, yet by the law of sympathy which permeates the entire string, it vibrates in ten sections of one-tenth each, all vibrating in unison. This is what gives the harmonic note its peculiar brilliancy. [Scientific Basis and Build of Music, page 92]
Hughes
If the laws which I shall endeavour to explain develope the twelve major harmonies, with each note in succession expanding its six tones from within itself; and if each of these is found to be a lower development, which leads the ear to a corresponding higher expansion of the twelve major key-notes, and the six tones of each ascending and descending in an unbroken sequence from any twelve consecutively, the thirteenth being the octave of the first, which commences a higher or a lower series; and if the twelve minor harmonies are also gained by the same laws from their twelve relative key-notes (the thirteenth again being octave): if, again, all other notes are shown to be but higher or lower repetitions of these twenty-four harmonies—may we not consider the problem as in some measure solved? especially as the harmonies proceed in geometric as well as harmonical ratio, and an accurate parallel can be traced between the development of notes and colours, which latter correspond with all the intricacies of harmonic sounds. [Harmonies of Tones and Colours, The Method of Development or Creation of Harmonies3, page 17]
See Also
14.13 - Full Harmonic Chord
14.22.1 - Enharmonic is the High Neutral
8.17 - Law of Harmonic Vibrations
8.22 - Law of Harmonic Pitch
9.23 - Circular Harmonic Orbit
9.24 - Elliptical Enharmonic Orbit
acute harmonics
Analytic Study of Harmonic Intervals
Degree of Harmonicity
diatonic and enharmonic ring
diatonic enharmonic
Eleventh Harmonic
Enharmonic
enharmonic current
enharmonic diesis
enharmonic scale
Enharmonic Sixth
enharmonic sixths
enharmonic third
enharmonic thirds
Full Harmonic Chord
grave harmonic
Harmonic
harmonic attractive chord
harmonic circles
harmonic combination
harmonic current
harmonic fifth
harmonic note
harmonic partial
harmonic progression
harmonic scale
Harmonic Series
harmonic sixths
harmonic third
Harmonic Thirds
harmonic undulatory
harmonical parallel
harmonical ratio
harmonical triad
harmonicity
harmonics
Helmholtz Subharmonic Series
inharmonic
Law of Harmonic Attraction and Repulsion
Law of Harmonic Pitch
Law of Harmonic Relationship
Law of Harmonic Vibrations
major harmonics
minor harmonics
polar harmonic current
Power of Beat Harmonics
progression of harmonics
scale of Harmonics
second atomic harmonic
subharmonic
superharmonic
synthesising current
Table of Plate Harmonics and Intervals
three harmonics
Twelth Harmonic
Vibrating Rod Harmonics