| Entropy | Entropy | |
Sympsionics Symbol | ||
Mutually dispersive, radiant. Fleeing from a common center. Mutual repulsion. Russell's Mother, Radiation, Magnetic or Radiant Energy and Keely's Positive Propulsion.
Keely
"The positive vibrations are the radiating or propulsive, the negative vibrations are the ones that are attracted towards the neutral center. The action of the magnetic flow is dual in its evolutions, both attractive and propulsive. The sound vibrations of themselves have no power whatever to induce dissociation, even in its lowest form. Certain differential, dual, triple and quadruple chords give introductory impulses which excite an action on molecular masses, liquid and gaseous, that increase their range of molecular motion and put them in that receptive state for sympathetic vibratory interchange which favors molecular disintegration, then, as I have shown, the diatonic enharmonic is brought into play, which further increases the molecular range of motion beyond fifty percent of their diameters, when molecular separation takes place, giving the tenuous substance that is necessary to induce progressive subdivision. This molecular gaseous substance, during its evolution, assumes a condition of high rotation in the sphere or tube in which it has been generated, and becomes itself the medium, with the proper exciters, for further progressive dissociation. The exciters include an illuminated revolving prism, condenser, and colored lenses, with a capped glass tube strong enough to carry a pressure of at least one thousand pounds per square inch. To one of these caps a sectional wire of platinum and silver is attached; the other cap is attached to the tube so screwed to the chamber as to allow it to lead to the neutral center of said chamber." [Snell Manuscript - The Book, ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS, page 6]
Professor Daniel Brinton
"The rhythmic relations in which force acts are everywhere, under all conditions, and at all times, the same. They are found experimentally to be universally expressible by the mathematical relations of thirds.
"These threefold relations may be expressed with regard to their results as,
I. Assimilative (Concentration, Gravitation)
II. Individualizing (Radiation, Entropy)
III. Dominant or Resultant
"From these three actions are derived the three fundamental LAWS OF BEING:
I. Law of Assimilation: every individualized object assimilates itself to all other objects.
II. Law of Individualization: every such object tends to assimilate all other objects to itself.
III. Law of the Dominant: every such object is such by virtue of the higher or dominant force which controls these (above) two tendencies. [14.09 - Brintons Laws of Being]
Entropy has often been loosely associated with the amount of order, disorder, and/or chaos in a thermodynamic system. The traditional qualitative description of entropy is that it refers to changes in the status quo of the system and is a measure of "molecular disorder" and the amount of wasted energy in a dynamical energy transformation from one state or form to another. In this direction, several recent authors have derived exact entropy formulas to account for and measure disorder and order in atomic and molecular assemblies. One of the simpler entropy order / disorder formulas is that derived in 1984 by thermodynamic physicist Peter Landsberg, based on a combination of thermodynamics and information theory arguments. He argues that when constraints operate on a system, such that it is prevented from entering one or more of its possible or permitted states, as contrasted with its forbidden states, the measure of the total amount of 'disorder' in the system is given by the first equation. Similarly, the total amount of "order" in the system is given by the second equation.
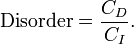
Disorder - Entropy (click to enlarge) |
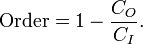
Order - Syntropy (click to enlarge) |
In which CD is the "disorder" capacity of the system, which is the entropy of the parts contained in the permitted ensemble, CI is the "information" capacity of the system, an expression similar to Shannon's channel capacity, and CO is the "order" capacity of the system. Wikipedia, Order and Disorder
See Also
Dynaspheric Force
Entropy
etheric seeks center
Figure 2.12.1 - Polarity or Duality
Gravism
Gravity
Law of Assimilation
Order
Ramsay - The Great Chord of Chords, the Three-in-One17
Rhythmic Balanced Interchange
Syntropy
Table of Cause and Effect Dualities
NOTE: (In Keely's jargon positive and negative are directly opposite to Russell's use of those same terms. To Keely positive = entropy and negative = syntropy. With Russell positive = syntropy and negative = entropy. Hence we would like to NOT USE either of the terms "positive" and "negative", instead use the terms "syntropy" (to center) and "entropy" (from center) to eliminate or at least reduce confusion.) The same holds true for the terms "male" and "female". See Figure 2.12.1 - Polarity or Duality for correspondences to these terms.
See Also
Entropy
Negative
Negative Accelerator
negative attraction
Negative Electricity
Negative Energy
Negative Entropy
Negative Refraction
positive
positive attraction
Positive electricity
Positive Negative
Sympathetic Positive Propulsion
Syntropy

See Also
2.19 - Male-Father and Female-Mother Forces
9th octave radioactive elements
Anode
Cathode
Chaos
Death
decay
decay-promoting
Decentralization
Decentrate
decomposive atomic energy
decomposive energy
destroy
destruction
destructive energy
destructive force
destructive interference
destructive
discharge
discharged body
discharging mass
discharging
Discord
disintegrate
Dispersion
dissociation
dissonance
electro-negative discharging system
entropy
female
feminine
Figure 12.04 - Locked Potential Points Relations and Descriptions
Figure 12.10 - Russells Locked Potential Wave
Figure 12.11 - Russells Locked Potential Full Ten Octave Gamut
Figure 16.03 and Figure 16.04 - Electricity as Charged Life and Discharged Death
Figure 9.12 - Scale of Locked Potentials over Time
growth-destroying
indestructibility of mass
indestructibility of matter
Ion
Isentropic
Law of Repulsion
life-destroying
life-negating
life-removing forces
Magnetism
Mother
mother
Negative Accelerator
negative attraction
negative discharge
Negative Electricity
Negative Energy
Negative Entropy
Negative Refraction
Negative
non-destructive testing
oligodynamic
Order and Disorder
point of discharge
Positive
Predominantly Entropy
Radiation
re-destructive
state of turmoil
Syntropy
Ultrasonic Non-Destructive Testing
Vacuum