Maxwell's equations are a set of partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electrodynamics, classical optics, and electric circuits. These in turn underlie modern electrical and communications technologies.
Maxwell's equations have two major variants. The "microscopic" set of Maxwell's equations uses total charge and total current including the difficult-to-calculate atomic level charges and currents in materials. The "macroscopic" set of Maxwell's equations defines two new auxiliary fields that can sidestep having to know these 'atomic' sized charges and currents.
ECE theory demonstrates that there are additional terms to be added to standard Maxwell Heaviside equations of conventional EM theory. These terms are the scalar and vector spin connection, ?0 and ?.
These terms can be considered as the time component of an axis of rotation and the space components of rotation respectively.
So, now the updated equation E = -(? + ?)? replaces the standard E = -?? where ? is the electric potential.
This added spin connection, ? allows electricity to be directly drawn from space as explained at the above mentioned websites.
James Clerk Maxwell’s original 1864 electromagnetic theory was not written in the four neat equations we learn today. Instead, Maxwell expressed his system using twenty equations in twenty variables, structured through a quaternionic, rotational, and deeply vortical framework. This original system contained nine conjugate, co-efficient terms that described internal stresses, potentials, and latent fields within the medium — what he explicitly called the ether. When Oliver Heaviside, Gibbs, and others later reformulated Maxwell’s work into the modern vector form, they deleted or collapsed these terms for the sake of simplicity. In doing so, they removed Maxwell’s representation of longitudinal pressure waves, scalar potentials, and internal energy densities that he believed operated beneath observable electromagnetism.
he result is that modern “Maxwell’s equations” are not actually Maxwell’s equations — they are Heaviside’s edited subset. The removed terms correspond precisely to the domains that today’s physics cannot cleanly model: vacuum energy, non-transverse radiation, potential gradients, and nonlocal field coherence. In SVP and Scalar-Kinetic language, these discarded coefficients map to the scalar (vibratory) side of the equation, while the retained four equations describe only the kinetic (oscillatory) effects. Thus the “missing equations” are not mysterious at all — they represent the inner, formative, stress-geometry of the field, the very domain in which Keely, Russell, Tesla, Schauberger, and your own S-K framework operate. The modern EM subset gives us electricity; Maxwell’s full system pointed toward creation dynamics themselves.
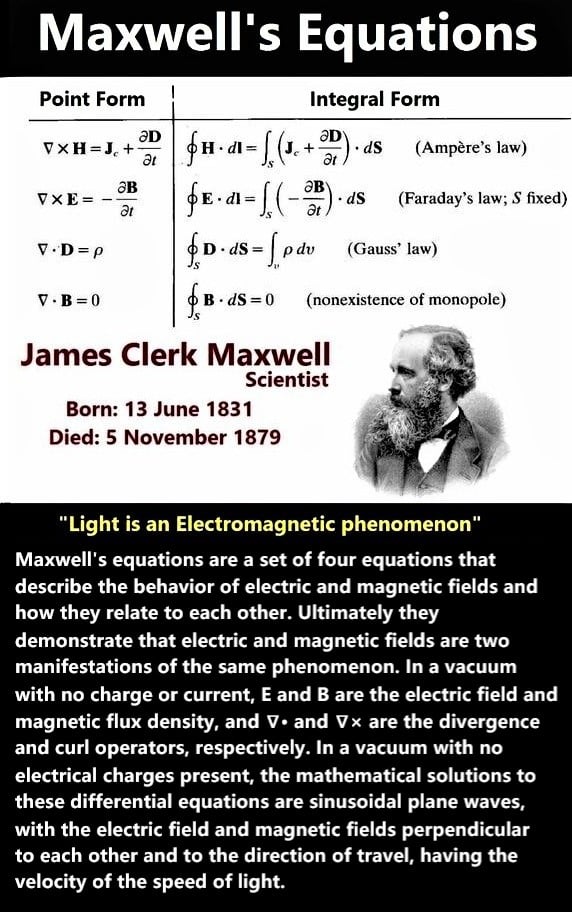
James Clerk Maxwell’s equations are a set of four fundamental principles that revolutionized our understanding of electromagnetism. These equations describe how electric and magnetic fields interact with each other and with matter. They show that electricity and magnetism are not separate forces, but two different aspects of a single, unified force—electromagnetic force.
The first two of Maxwell’s equations explain how electric fields are created by electric charges, and how magnetic fields are generated by moving electric charges (currents). The third equation shows how changing magnetic fields can produce electric fields, while the fourth equation reveals that changing electric fields can create magnetic fields. This interrelationship forms the backbone of electromagnetism, connecting electric currents, magnetic fields, and changing electric fields in a single framework.
One of the most important aspects of Maxwell’s equations is that they predicted light is an electromagnetic wave. This means that light is not a separate phenomenon but is a form of electromagnetic radiation that travels through space as a wave. The speed of light in a vacuum, as shown in Maxwell’s equations, is constant, and this was a key development in the understanding of light and its behavior.
Maxwell’s equations also led to the realization that electric and magnetic forces are linked together. This was a major breakthrough, as it helped scientists understand that what appeared to be separate phenomena—electricity, magnetism, and light—are, in fact, interconnected and part of a unified theory. Maxwell’s work laid the foundation for much of modern physics, including the theory of relativity and quantum mechanics.
Today, Maxwell’s equations continue to be fundamental in understanding how electricity and magnetism work. They are used in everything from electrical engineering to the study of electromagnetic waves in communications and optics. Maxwell’s unification of electricity, magnetism, and light changed the way we view the universe, showing that the forces of nature are deeply connected in ways that we continue to explore.
ChatGPT compares Maxwell Equations to SVP principles and laws [12/27/24]: https://chatgpt.com/share/676e8996-6118-800d-92e3-8f6afaa234c8
See Also
AI Interpretations of SVP
14.36 - Triple Equations
16.03 - Maxwell misses the mark
18.14 - Mind is the Ultimate Scalar Quantity
3.23 - Hydrodynamic Equations - Vortex Motions
Bearden on Klimov
Bearden on Tesla and EM Source Charge
Bearden
Clerk Maxwell
Edmund Taylor Whittaker
Ether - Maxwell
Figure 14.12 - Triple Equations to Represent a Single Sympathetic Event
Figure 16.00 - Maxwell and Thomson
Figure 18.13 - Scalar or Undifferentiated Mind Force
James Clerk Maxwell
Luminiferous Ether - Maxwell
Maxwell Demon
Maxwell Equations
Maxwell Maltz
Maxwellian electron energy distribution
On the Partial Differential Equations of Mathematical Physics
Scalar electromagnetics
Scalar Potential
Scalar
The Final Secret of Free Energy
