The volt (symbol: V) is the SI derived unit of electromotive force, commonly called "voltage". It is also the unit for the related but slightly different quantity electric potential difference (also called "electrostatic potential difference"). It is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745-1827), who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery. (Wikipedia)
SI multiples for volt (V) | |||
Value | Symbol | Name | Multiples |
| 1024 V | YV | yottavolt | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| 1021 V | ZV | zettavolt | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| 1018 V | EV | exavolt | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| 1015 V | PV | petavolt | 1,000,000,000,000,000 |
| 1012 V | TV | teravolt | 1,000,000,000,000 |
| 109 V | GV | gigavolt | 1,000,000,000 |
| 106 V | MV | megavolt | 1,000,000 |
| 103 V | kV | kilovolt | 1,000 |
| 101 V | daV | decavolt | 10 |
| 100 V | V | volt | 1 |
| 10-3 V | mV | millivolt | 1/1,000 |
| 10-6 V | µV | microvolt | 1/1,000,000 |
| 10-9 V | nV | nanovolt | 1/1,000,000,000 |
| 10-12 V | pV | picovolt | 1/1,000,000,000,000 |
| 10-15 V | fV | femtovolt | 1/1,000,000,000,000,000 |
| 10-18 V | aV | attovolt | 1/1,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| 10-21 V | zV | zettavolt | 1/1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| 10-24 V | yV | yoctovolt | 1/1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
electron v. (eV) - a unit of energy equal to the energy acquired by an electron in being accelerated through a potential difference of 1 volt; equal to 1.602 × 10−19 joule.
gigaelectron v. (GeV) - one thousand million electron volts (109 eV).
kiloelectron v. (keV) - one thousand electron volts (103 eV).
megaelectron v. (MeV) - one million electron volts (106 eV).
Read more: http://www.answers.com/topic/volt#ixzz1KL0aPi47
In the Russell paradigm volts are units of discharging electrical energy or entropy.
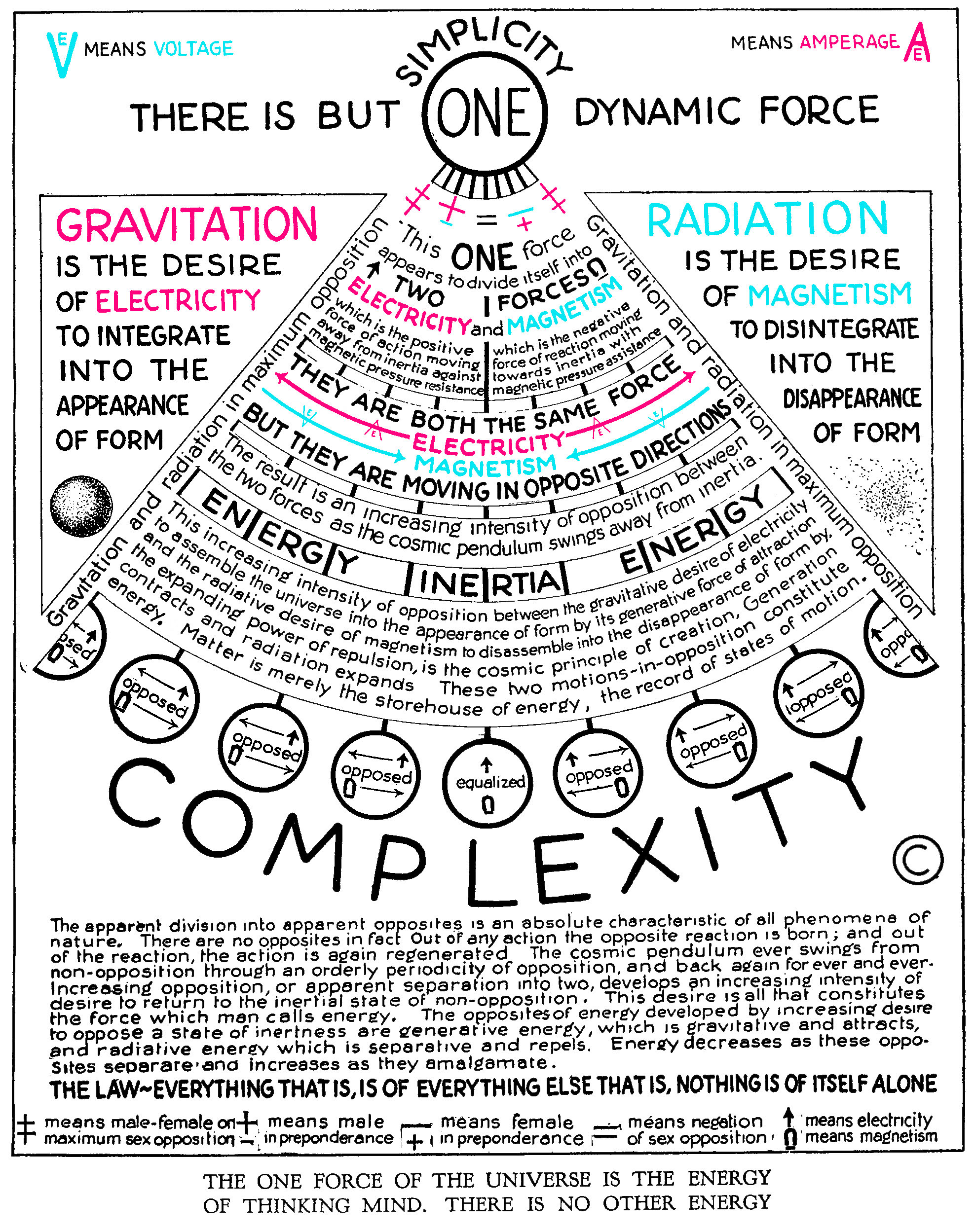
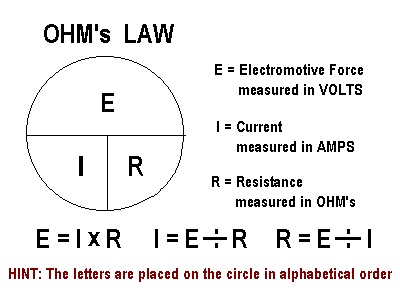
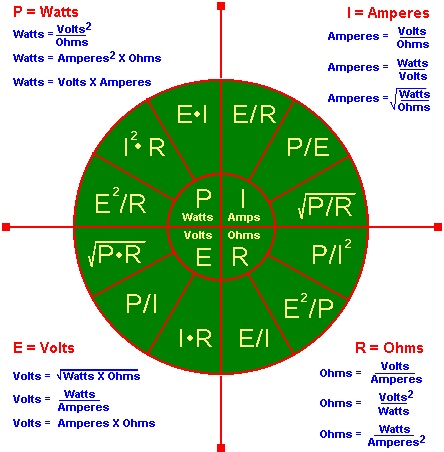
This new table is a beginning to develop tables as suggested by Keely in his Keelys Forty Laws. See Ampere
Russell multiples for volt (V) | |||
Indig | Symbol | Multiple | Entropy Potential |
| 4-- V | Vr4 | 83 | 512 |
| 3- V | Vr3 | 82 | 64 |
| 2- V | Vr2 | 81 | 8 |
| 1- V | Vr1 | 80 | 1 |
| 0 V | Vr0 | 00 | 0 |
In the The Universal One see pages 83, 163 and 173.
Schauberger
In every respect, experiments with this formative and levitative (synthesising) current produced surprising results. Thus, for example, 2,000,000 volts per drop of water, which were measurable, visible and palpable, and therefore incontrovertible, could be freed with appropriate charge-releasing devices. With 50 pairs of needle-jets about 200 million volts can be produced for virtually nothing, for which today's science requires giant machines. Even then it can only produce an exceptionally disintegrative (analysing) current, which has life-negating properties. This is to be differentiated from the formative and levitative, therefore life-affirming, functions of the synthesizing current mentioned elsewhere. [The Energy Evolution - Harnessing Free Energy from Nature, The Life-Current in Air and Water]
See Also
3 Phase Formula
Ampere
Electrical Potential
Electricity
Inverse Square Law
Ohm
Potential
Resistance
seed-volt
Square Law
Volt
Voltage
Watt
