The watt (pronounced wot; symbol: W) is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units (SI), named after the Scottish engineer James Watt (1736 - 1819). The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion. (wikipedia)
In terms of classical mechanics, one watt is the rate at which work is done when an object's velocity is held constant at one meter per second against constant opposing force of one newton.
In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which work is done when one Ampere (A) of current flows through an electrical potential difference of one volt (V).
SI multiples for watt (W) | |||
Value | Symbol | Name | Multiples |
| 1024 W | YW | yottawatt | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| 1021 W | ZW | zettawatt | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| 1018 W | EW | exawatt | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| 1015 W | PW | petawatt | 1,000,000,000,000,000 |
| 1012 W | TW | terawatt | 1,000,000,000,000 |
| 109 W | GW | gigawatt | 1,000,000,000 |
| 106 W | MW | megawatt | 1,000,000 |
| 103 W | kW | kilowatt | 1,000 |
| 102 W | hW | hectowatt | 100 |
| 101 W | daW | decawatt | 10 |
| 100 W | W | watt | 1 |
| 10-1 W | dW | deciwatt | 1/10 |
| 10-2 W | cW | centiwatt | 1/100 |
| 10-3 W | mW | milliwatt | 1/1,000 |
| 10-6 W | µW | microwatt | 1/1,000,000 |
| 10-9 W | nW | nanowatt | 1/1,000,000,000 |
| 10-12 W | pW | picowatt | 1/1,000,000,000,000 |
| 10-15 W | fW | femtowatt | 1/1,000,000,000,000,000 |
| 10-18 W | aW | attowatt | 1/1,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| 10-21 W | zW | zeptowatt | 1/1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| 10-24 W | yW | yoctowatt | 1/1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
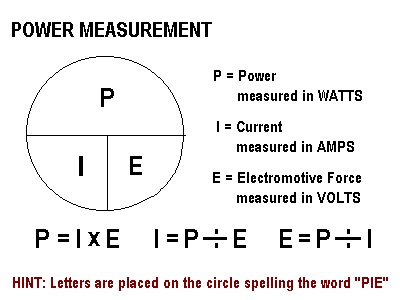
Ohm's Law
See Also
3 Phase Formula
Electromotive Force
horsepower
kilowatt
Ohms Law
Power
Resistance
Volt
