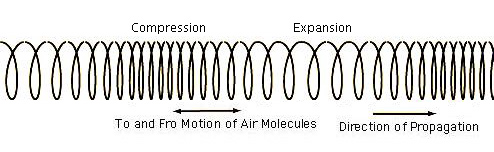
- Same as Compression Wave or Sound Wave. A wave incident or normal to a surface. One of many modes or dimensions of motion present in all vibrations and oscillations. Generally, considered as a motion to and from a center or source. When harmonic is considered syntropic and when enharmonic considered entropic.
- "Vibration in which the principal motion is in the direction of the longest dimension." (Rossing, Thomas D.; The Science of Sound; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, 1982.)
- "A vibrating medium must lengthen and shorten 2 times per each lateral (transverse) oscillation; so 1 longitudinal equals 2 lateral or (transverse). Longitudinal frequencies are independent of string tension." (Tyndall, John; Sound; Longmans, Green, and Co., London, 1893.)
Longitudinal Axis
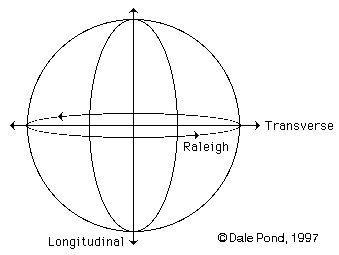
Triple axis of the three modes of vibration drawn to reference a circle and sphere.
The three modes working together develop rotation by and through each other's motion - the rotation is the Rayleigh Wave or Surface Wave mode. The first two modes cause (or are) straight line and zig-zag motions only. The third or Rayleigh Wave is circular.
Longitudinal Axis
Longitudinal Waves, Velocity of
See Also
8.3 - Conventional View of Wave Motion
Compression Wave
Compression Wave Velocity
Figure 8.2 - Compression Wave Phase Illustration
Figure 9.11 - Compression Wave with expanded and contracted Orbits
Longitudinal Wave
Modes of Vibration
Sine Wave
Sound
Wave
Wave Field
