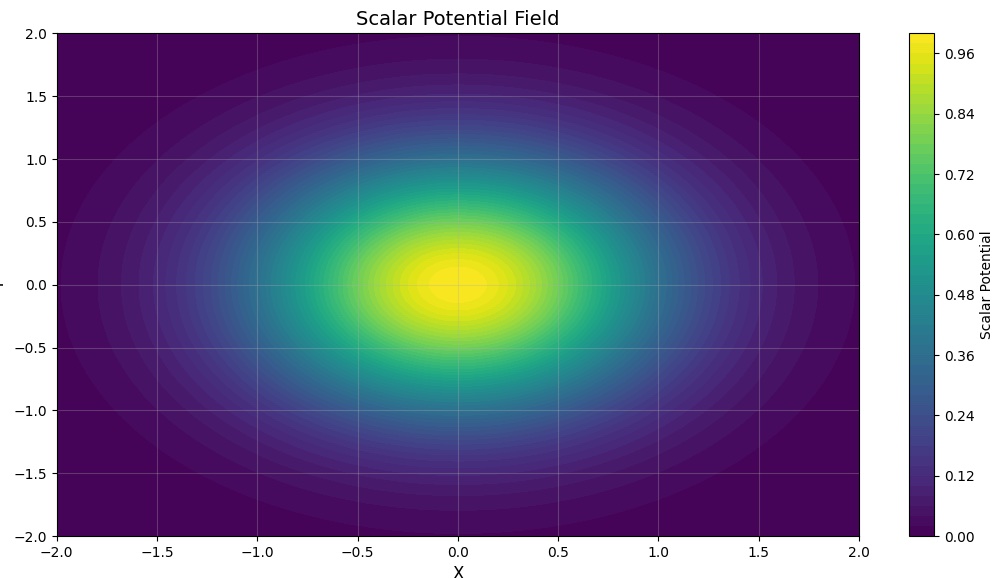
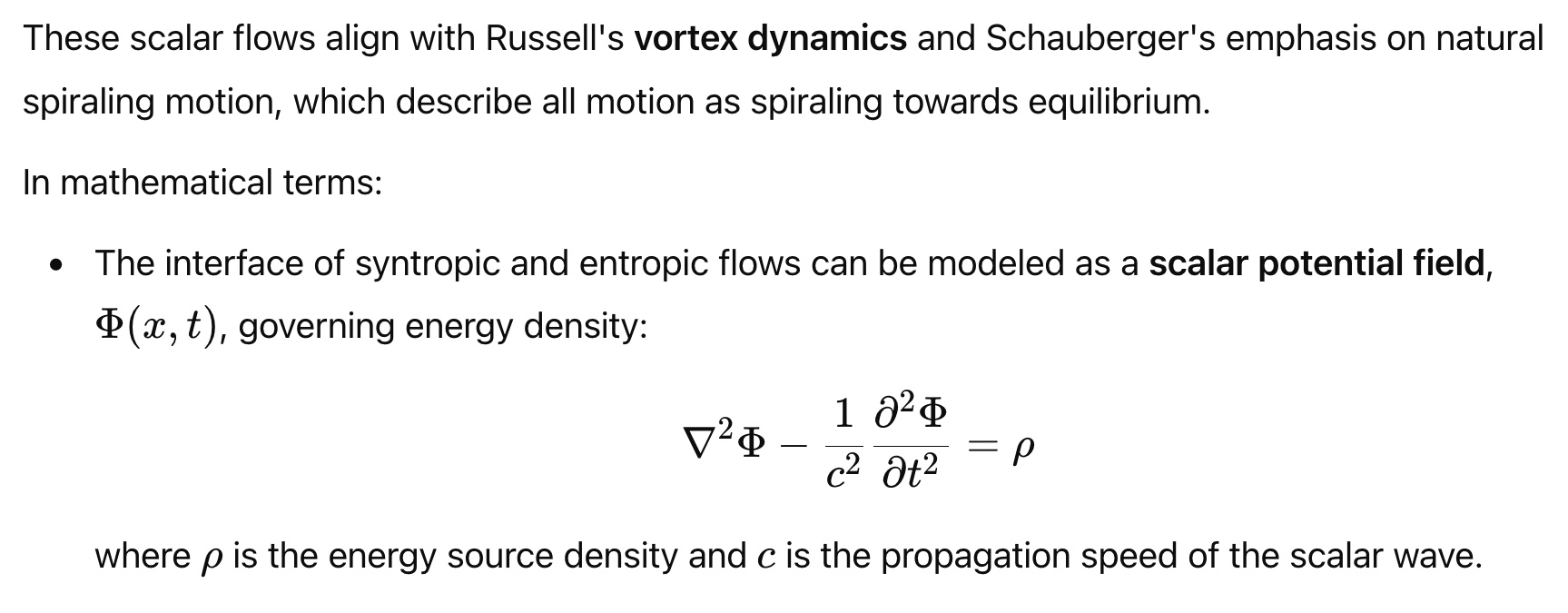
A scalar field is a mathematical function that assigns a single numerical value, known as magnitude, to every point in space. Unlike vector fields, scalar fields do not have directional properties. Examples of scalar fields include temperature, electric potential, and pressure. At each point in space, the scalar field provides a value that can vary from one point to another but remains directionless. Scalar fields are fundamental in both classical and quantum physics, helping to describe phenomena like gravitational potential and mass distributions in an intuitive manner.
Clarifying the Concept: Scalar Field via Bifilar Coil
A scalar field, in Keely–Bearden–Tesla terms, is:
non-radiative
non-translating
internally dynamic (vibration, not oscillation)
a field of potential, not vector force
usually generated by symmetry and cancellation
Why Bifilar?
A bifilar coil (Tesla-style) has two windings wound in parallel in the same direction. If pulsed in counterflow (equal and opposite), then the EM vectors cancel, but the potential difference and stress remain. This can:
Compress or rarefy the dielectric aether (scalar potential)
Generate longitudinal waves under sudden potential change (Bearden)
Form a field not detectable by a standard EM probe, but one that can affect nearby matter, especially if sympathetically tuned.
This is the scalar field: no magnetic component escaping, no oscillatory transverse wave, but internal vibratory stress.
In Wave Dynamics:
1. Antiphase (180° out of phase)
• Two waves oppose crest-to-trough.
Interaction: Destructive interference — amplitude diminishes or cancels.
Conventional physics: simple cancellation.
SVP view: an entropic relation — mutual opposition leading toward dissolution of motion.
2. Phase Conjugation
• A wave is reversed in time, retracing its path, undoing distortions.
Interaction: restores coherence, repairs losses, symmetry reappears.
Conventional physics: nonlinear optics, time-reversed EM or acoustic wave.
SVP view: a syntropic relation — return toward scalar potential, a restorative symmetry.
3. Neutralization
• Not merely opposition, and not just reversal — but a resting back into the zero-point.
Interaction: opposing polarities or phases resolve into the Neutral Center.
Conventional physics: no direct equivalent (closest is complete cancellation to zero).
SVP view: the functional pivot — where oscillations and vibrations merge back into scalar quiescence. Neutralization isn’t destruction; it’s re-harmonization back into undifferentiated equilibrium.
So we might say:
Antiphase = cancel by opposition (entropy).
Phase Conjugation = restore by reversal (syntropy).
Neutralization = reconcile into stillness (Dominant / Neutral Center).
In Keely’s framework, “neutralization” is the most powerful of the three because it doesn’t just erase — it returns motion to source (Zero Point, stillness, Void) where it becomes latent - ready to be activated when disturbed.
See Also
AI Interpretations of SVP
Scalar Potential
18.14 - Mind is the Ultimate Scalar Quantity
Bearden Scalar Wave
Dale Pond on Scalar Potential - TeslaTech 2011
Differentiating Scalar Potential to Kinetic Motion - Part 1
Differentiating Scalar Potential to Kinetic Motion - Part 2
electrostatic scalar potential
Engineering Scalar Forces
Figure 18.13 - Scalar or Undifferentiated Mind Force
Keely Transforming Scalar Potential into Kinetic Forces
List of Synonyms for Scalar
magnetostatic scalar potential
Mind and Mind Force as Scalar Potential
Mind Force the hidden Scalar Force
Scalar - Eric Dollard
Scalar Differentiator
scalar electromagnetic potential
Scalar electromagnetics
scalar field
Scalar
Transforming Scalar to Kinetic
