This process is commonly referred to as the "Quantum Leap" wherein force, as measured in a unit of a "photon" is absorbed (syntropy or negentropy) causing an orbiting electron to 'leap' to the next innermost "electron shell" or a photon's energy equivalent is given up (entropy) and the electron leaps to the next outermost "electron shell". It must be noted the "orbiting Electron Theory" is in question and most likely the electron does not exist as a discrete "thing" but are instead and more accurately a discrete quantity of least possible electric charge. Since the most prevalent theory is more or less dead we propose a closer examination of Keely's morphology which is supported, in its basics, by logic and Richard Feynman's theoretical work.
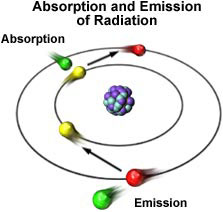
Figure 3.37 - Successive Centralizations or Quantum Leap
(courtesy Indiana University, Purdue University, Indiana)
(click to enlarge)
See Also
Centralization
velocity of rotating etheric stream
See Also
Centralization
Law of Assimilation
Laws of Being
Negative Attraction
Syntropy
water-inwinding suctional force
3.21 - Successive Centralizations
4.11 - Matter is Centralized Condensed and Differentiated Light
7.1 - Matter is centralized motion
balance
centralization
equilibrium
Figure 2.11 - Center Seeking and Center Fleeing
Figure 3.25 - Celestial Seeks and Condenses at Center
Figure 3.33 - Syntropy Seeking Center - Entropy Fleeing from Center
Figure 3.37 - Successive Centralizations or Quantum Leap
Figure 4.13 - Triplet Originations and Centralizations of Matter
inwind
New Concept - Wobbling Gyroscopes Seek Balance
New Concept - XXXVI - Wobbling Gyroscopes Seek Balance
syntropy
