In particle physics, the Dirac equation is a relativistic wave equation derived by British physicist Paul Dirac in 1928. In its free form, or including electromagnetic interactions, it describes all spin-½ massive particles such as electrons and quarks for which parity is a symmetry. It is consistent with both the principles of quantum mechanics and the theory of special relativity, and was the first theory to account fully for special relativity in the context of quantum mechanics. It was validated by accounting for the fine details of the hydrogen spectrum in a completely rigorous way.
The equation also implied the existence of a new form of matter, antimatter, previously unsuspected and unobserved and which was experimentally confirmed several years later. It also provided a theoretical justification for the introduction of several component wave functions in Pauli's phenomenological theory of spin. The wave functions in the Dirac theory are vectors of four complex numbers (known as bispinors), two of which resemble the Pauli wavefunction in the non-relativistic limit, in contrast to the Schrödinger equation which described wave functions of only one complex value. Moreover, in the limit of zero mass, the Dirac equation reduces to the Weyl equation.
Although Dirac did not at first fully appreciate the importance of his results, the entailed explanation of spin as a consequence of the union of quantum mechanics and relativity—and the eventual discovery of the positron—represents one of the great triumphs of theoretical physics. This accomplishment has been described as fully on a par with the works of Newton, Maxwell, and Einstein before him. In the context of quantum field theory, the Dirac equation is reinterpreted to describe quantum fields corresponding to spin-½ particles. Wikipedia, Dirac Equation
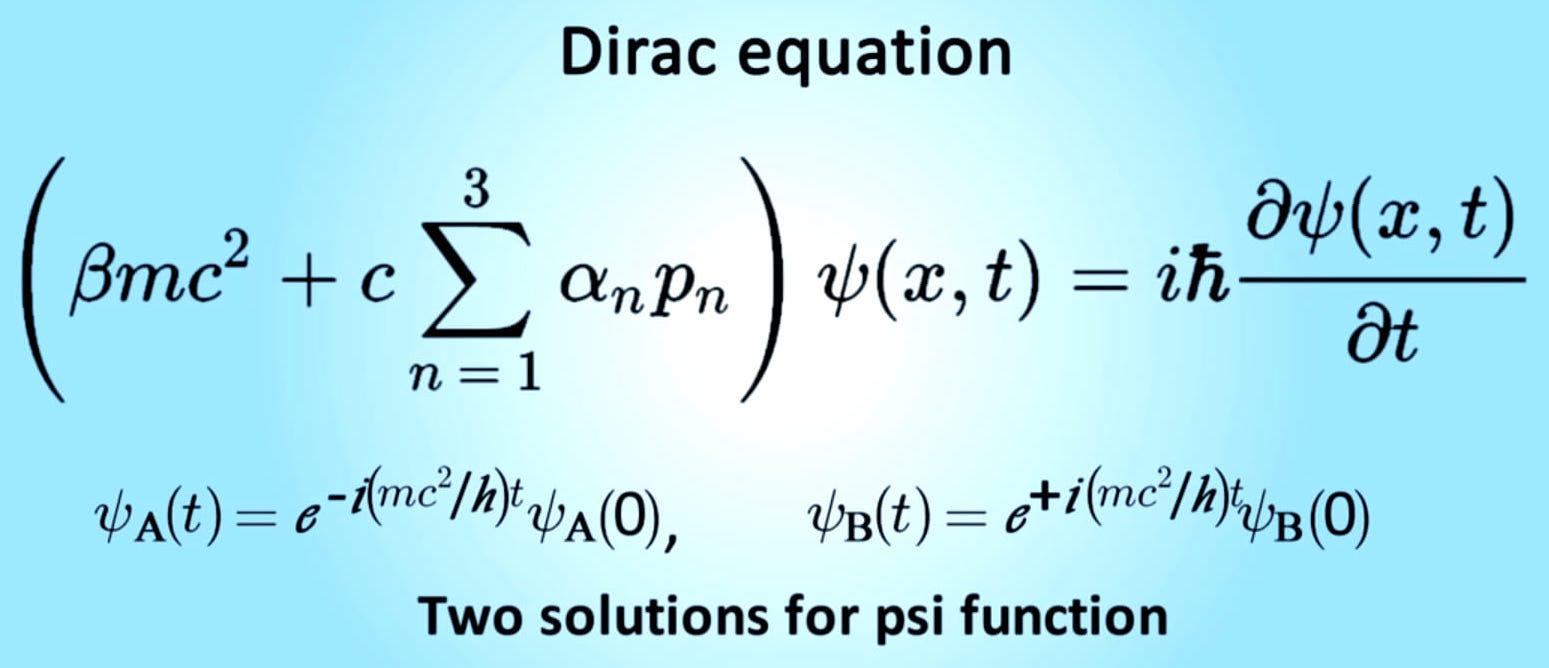
The Dirac equation is:
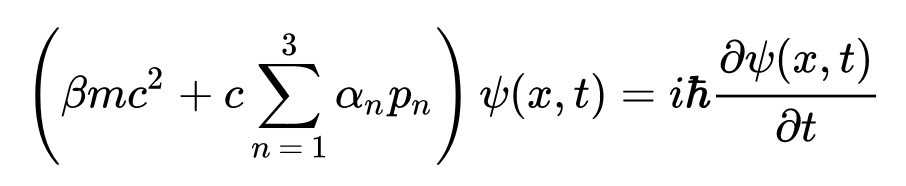
She said: "Tell me something nice"
He said : ( ? + m) Él = 0
This is Dirac's equation, and it's the most beautiful of all physics. Describes the phenomenon of quantum entanglement.
“If two systems interact with each other for a certain period of time and then come apart, we can describe them as two different systems, but in a subtle way they become a single system.” "What happens to one continues to affect the other, even light-years away."
This is quantum entanglement or quantum connection. Two particles that, at some point, were connected, are still somehow connected. The distance between the two doesn't matter, even if they are at opposite ends of the Universe. The connection between them is instantaneous. It is the same thing that happens between two people when they are bonded by a bond that only living beings can experience. That's how this relationship we call LOVE works. [anon]
See Also
Compound Interetheric
Dirac Sea
Interetheric
Law of Sympathetic Association
Law of Sympathetic Oscillation
Law of Sympathetic Vibration
Paul Dirac
sympathy
sympathetic association
sympathetic oscillation
sympathetic vibration
