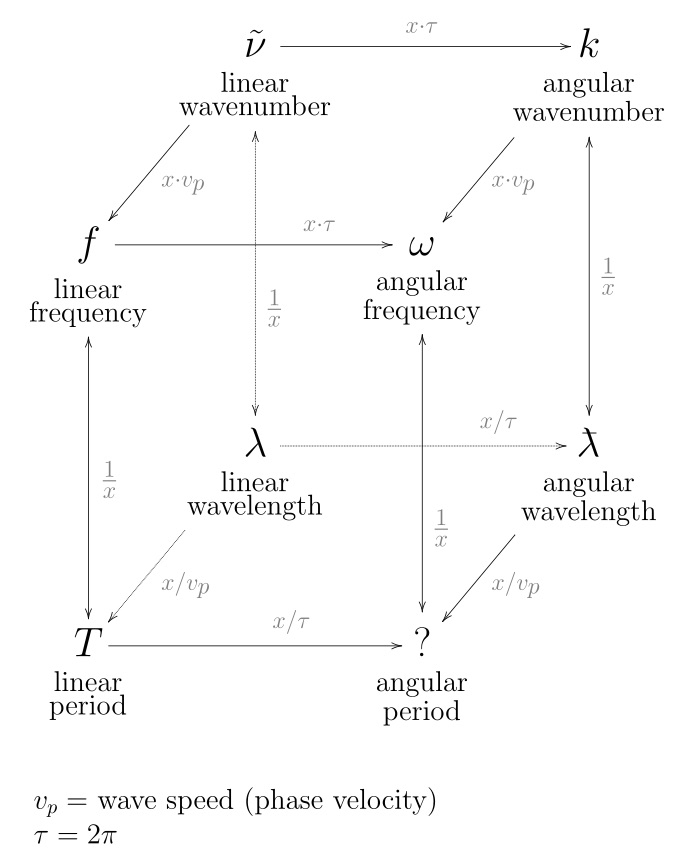
In the physical sciences, the wavenumber (also wave number or repetency) is the spatial frequency of a wave, measured in cycles per unit distance or radians per unit distance. Whereas temporal frequency can be thought of as the number of waves per unit time, wavenumber is the number of waves per unit distance.
In multidimensional systems, the wavenumber is the magnitude of the wave vector. The space of wave vectors is called reciprocal space. Wave numbers and wave vectors play an essential role in optics and the physics of wave scattering, such as X-ray diffraction, neutron diffraction, and elementary particle physics. For quantum mechanical waves, the wavenumber multiplied by Planck's constant is the canonical momentum.
Wavenumber can be used to specify quantities other than spatial frequency. In optical spectroscopy, it is often used as a unit of temporal frequency assuming a certain speed of light. Wikipedia, Wavenumber
The reciprocal of wavelength is known as the wave number (N) and since it is directly proportional to frequency can therefore be used exactly as frequency would be used. Wave number denotes the number of waves per centimeter.
wave number = velocity (c) divided by wavelength (l).
6/28/01:
Frequency is the number of cycles per TIME.
Wave Number is the number of cycles per SPACE.
Wavelength is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase.
See Also
Frequency
Interval
Oscillation
Pitch
Revolution
Rotation
Space
Spacetime
Table 12.02.01 - Wavelengths and Frequencies
Time
Unison
Wave Field
Wave
Wavelength
