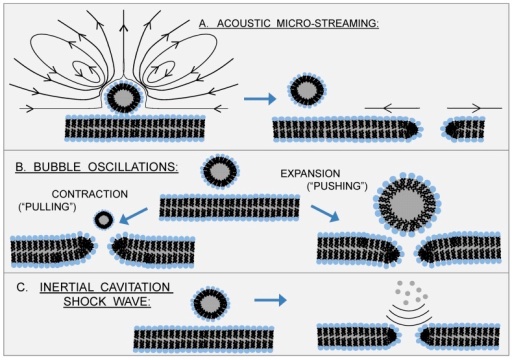
Sonoporation, or cellular sonication, is the use of sound (typically ultrasonic frequencies) for modifying the permeability of the cell plasma membrane. This technique is usually used in molecular biology and non-viral gene therapy in order to allow uptake of large molecules such as DNA into the cell, in a cell disruption process called transfection or transformation. Sonoporation employs the acoustic cavitation of microbubbles to enhance delivery of these large molecules. The bioactivity of this technique is similar to, and in some cases found superior to, electroporation. Extended exposure to low-frequency (<MHz) ultrasound has been demonstrated to result in complete cellular death (rupturing), thus cellular viability must also be accounted for when employing this technique.
Sonoporation is under active study for the introduction of foreign genes in tissue culture cells, especially mammalian cells. Sonoporation is also being studied for use in targeted Gene therapy in vivo, in a medical treatment scenario whereby a patient is given modified DNA, and an ultrasonic transducer might target this modified DNA into specific regions of the patient's body. Wikipedia, Sonoporation
