The resonant frequencies of air columns depend upon the speed of sound in air as well as the length and geometry of the air column. Longitudinal pressure waves reflect from either closed or open ends to set up standing wave patterns. Important in the visualization of these standing waves is the location of the nodes and antinodes of pressure and displacement for the air in the columns. from http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/hframe.html
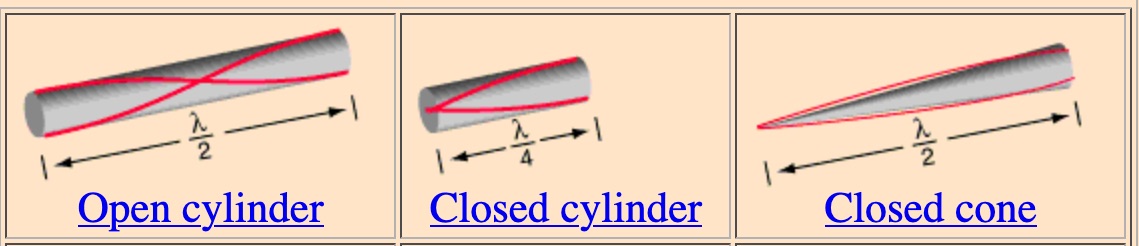
courtesy HyperPhysics
See Also
5.2 - Vortex Motions in Resonators
air column resonance
Cavity Resonator
double column
Figure 6.17 - Areas and Volumes - Relations and Proportions
Helmholtz Resonator
organ pipe
Resonance
Resonator
Table 12.02 - Length Area and Volume Math
Volumetric Resonator
