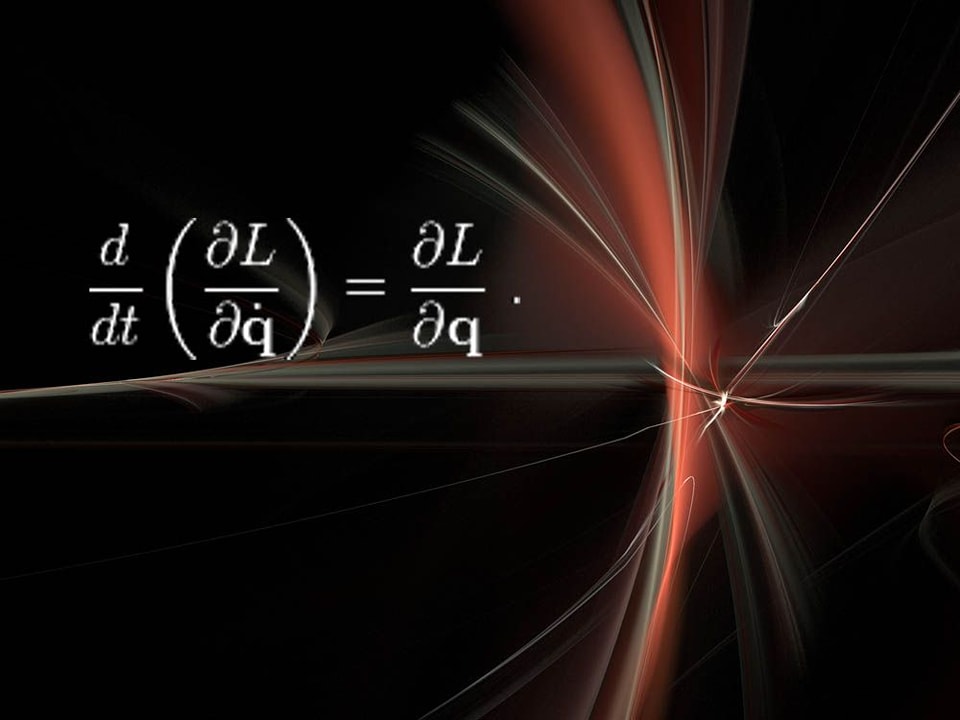
Meet Euler Lagrange Equation!
Solving this equation tells you how the system will evolve with time. This theorem is astonishingly elegant work of Emmy Noether and this is really fundamental intuition in physics to know the role of symmetry. if your system has a symmetry, then there is a corresponding conservation law. For example, the idea that the fundamental laws of physics are the same today as tomorrow (time symmetry) implies that energy is conserved. The idea that the laws of physics are the same here as they are in outer space implies that momentum is conserved. Symmetry is perhaps the driving concept in fundamental physics, primarily due to Noether's contribution. The L in this equation is lagrangian and is the difference of Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy.
In the calculus of variations and classical mechanics, the Euler–Lagrange equations is a system of second-order ordinary differential equations whose solutions are stationary points of the given action functional. The equations were discovered in the 1750s by Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler and Italian mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange.
Because a differentiable functional is stationary at its local extrema, the Euler–Lagrange equation is useful for solving optimization problems in which, given some functional, one seeks the function minimizing or maximizing it. This is analogous to Fermat's theorem in calculus, stating that at any point where a differentiable function attains a local extremum its derivative is zero.
In Lagrangian mechanics, according to Hamilton's principle of stationary action, the evolution of a physical system is described by the solutions to the Euler equation for the action of the system. In this context Euler equations are usually called Lagrange equations. In classical mechanics, it is equivalent to Newton's laws of motion, but it has the advantage that it takes the same form in any system of generalized coordinates, and it is better suited to generalizations. In classical field theory there is an analogous equation to calculate the dynamics of a field. Wikipedia, Euler Lagrange Equation
